🟠 A must-have template for creating a Rust project for microcontrollers.
CPU–Peripheral I/O Communication: Approaches and Trade-offs
🟠 Data Transmission Between CPU and Peripheral Devices via I/O Methods
MMIO (Memory-Mapped I/O)
MMIO (Memory-Mapped I/O) is a way for the central processing unit (CPU) to interact with peripheral hardware devices (e.g. UART, timers, GPIO, SPI, etc.) by "sticking" the registers of these devices to specific addresses in the CPU memory.
These addresses in the CPU do not store regular data, but allow reading and writing to the device control registers.
This means that the peripheral device can be accessed in the same way as regular memory - via regular memory read/write instructions (LDR, STR, MOV, etc.). at specific addresses.
Debugging firmware
Classic software development is always inside the cycle of write - run - check - fix.
In classic systems, debugging is simplified by built-in logs, breakpoints and step-by-step code execution directly in the IDE.
When developing programs for microcontrollers, debugging is significantly more complicated since the code is written on a PC and executed on a device with a completely different architecture.
Obtaining debug information, setting breakpoints, accessing registers and local variables require a special environment and integration of tools, and the process itself becomes much less obvious.
🟠 In this article I want to describe the standard process when debugging software running on a microcontroller and describe the tools that play a key role in this.
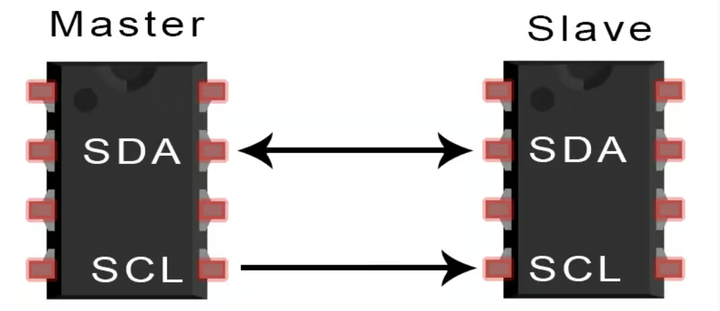
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit)
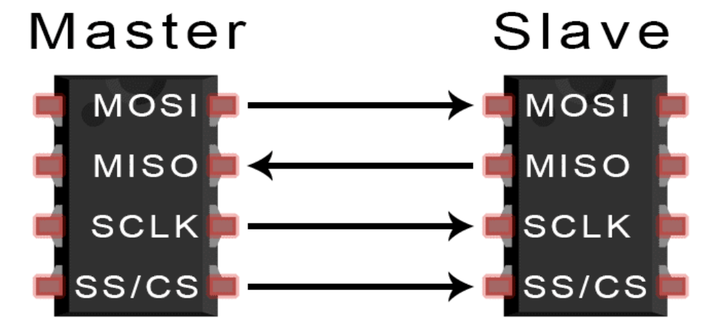
SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface)
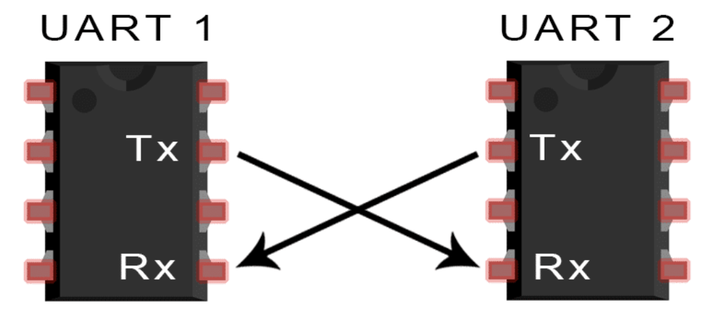
UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver / Transmitter)
Serial Protocols
Digital systems are based on the concept of bits, in addition to using bits they often have to transfer them back and forth usually between two components (MCU and Sensor, LCD etc).
🟠 All the different methods of bit transfer can be divided into 2 categories - Parallel and Serial transfer
Embedded 📦 crates ecosystem
Review of the ecosystem of crates used for programming microcontrollers in Rust
In general, developing programs for MCU is aimed at obtaining some information from the surrounding world, performing necessary calculations with this data and interacting back. Using Rust gives a huge freedom in choosing the level of abstraction at which the developer can interact with the MCU.
🟠 In this article I'll take a closer look at these abstraction levels and some other useful crates.
🧪 RP2040 Pico W Lab
Experiments, Prototypes & Notes with the Raspberry Pi Pico W
This repository contains my projects, experiments, and notes using the Raspberry Pi Pico W, built on the RP2040 microcontroller with integrated Wi-Fi.
It serves as a playground for testing ideas, learning embedded concepts, and building small prototypes.